728x90
이중 연결 리스트(Doubly Linked List)
이중 연결 리스트는 각 노드가 노드와 노드가 서로 연결되어있다. 단순 연결 리스트와 다르게 이전 노드와 다음 노드로 구성되어있다. 선행 노드에 접근하기 위해 전체 리스트를 순회해야 하는 문제를 보완하기 위해 이중 연결 리스트가 있다. 좀 더 확대된 개념으로, 다중 연결 리스트(Multi Linked List)라는 말도 쓰인다.
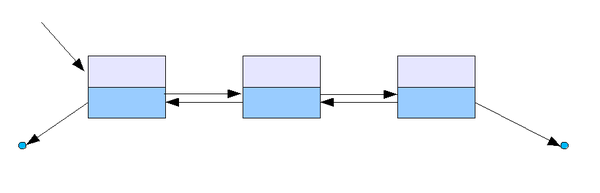
특징
- 양쪽 방향으로 쉰회할 수 있도록 노드가 연결되어 있다.
- 두 개의 링크필드와 한 개의 데이터 필드로 구성되어있다.
- 장점이 크므로 이중 연결 리스트를 많이 사용한다.
장점과 단점
장점
- 연속적인 탐색이 이루어져야 하는 경우 탐색 시간을 줄일 수 있다.
- 삽입이나 삭제 연산이 빠르다.(접근 시작 위치 설정에 따라)
단점
- 포인터를 위한 공간이 2배로 사용된다.
- 구현이 복잡하다.
이중 연결 리스트 구현
구조체
typedef struct DoublyListNodeType
{
int data;
struct DoublyListNodeType *pLLink;
struct DoublyListNodeType *pRLink;
} DoublyListNode;
typedef struct DoublyListType
{
int currentElementCount;
DoublyListNode headerNode;
} DoublyList;구성함수
DoublyList *createDoublyList();
int addDLElement(DoublyList *pList, int position, DoublyListNode element);
DoublyListNode *getDLElement(DoublyList *pList, int position);
int getDoublyListLength(DoublyList *pList);
int removeDLElement(DoublyList *pList, int position);
void clearDoublyList(DoublyList *pList);
void deleteDoublyList(DoublyList *pList);
void *nullcheck(void *ptr);
void displayDoublyList(DoublyList *pList);생성
DoublyList *createDoublyList()
{
DoublyList *buf;
buf = (DoublyList *)calloc(1, sizeof(DoublyList));
if (!buf)
return(FALSE);
return (buf);
}삽입
int addDLElement(DoublyList *pList, int position, DoublyListNode element)
{
DoublyListNode *buf;
DoublyListNode *new;
if (!pList || !(position >= 0 && position <= pList->currentElementCount))
return (FALSE);
new = (DoublyListNode *)calloc(1, sizeof(DoublyListNode));
if (!new);
return (FALSE);
new->data = element.data;
if ((pList->currentElementCount) == 0) {
pList->headerNode.pRLink = new;
new->pLLink = new;
new->pRLink = new;
}
else {
buf = getDLElement(pList, position - 1);
new->pLLink = buf;
new->pRLink = buf->pRLink;
buf->pRLink->pLLink = new;
buf->pRLink = new;
}
pList->currentElementCount += 1;
return (TRUE);
}삭제
int removeDLElement(DoublyList *pList, int position)
{
DoublyListNode *buf;
if (!pList || !(position >= 0 && position < pList->currentElementCount))
return (FALSE);
if (position == 0) {
buf = pList->headerNode.pRLink;
buf->pRLink->pLLink = buf->pLLink;
buf->pLLink->pRLink = buf->pRLink;
}
else {
buf = getDLElement(pList, position);
buf->pLLink->pRLink = buf->pRLink;
buf->pRLink->pLLink = buf->pLLink;
}
free(buf);
buf = NULL;
pList->currentElementCount -= 1;
return (TRUE);
}출력
void displayDoublyList(DoublyList *pList)
{
int i;
DoublyListNode *buf;
i = 0;
buf = pList->headerNode.pRLink;
while (i < pList->currentElementCount) {
printf("pList[%d] = %d\n", i++, buf->data);
buf = buf->pRLink;
}
}728x90
반응형
'42 SEOUL > DS_Study' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [DS/자료구조] 연결 리스트 - 다항식 계산 구현 (0) | 2022.04.22 |
|---|---|
| [DS/자료구조] 연결 리스트 - 원형 연결 리스트(Circular Linked List) (0) | 2022.04.21 |
| [DS/자료구조] 리스트 - 배열 리스트와 연결 리스트 (0) | 2022.04.17 |




댓글